Infill refers to the internal structure of a 3D printed object, and it plays a crucial role in determining its strength, weight, and printing time. When it comes to 3D printing, there are many factors that contribute to the quality and strength of the final printed object. One of these factors is infill. In this guide, we will explore the importance of infill in 3D printing and provide you with the knowledge you need to optimise your prints.
What is 3D printing infill and why is it important?
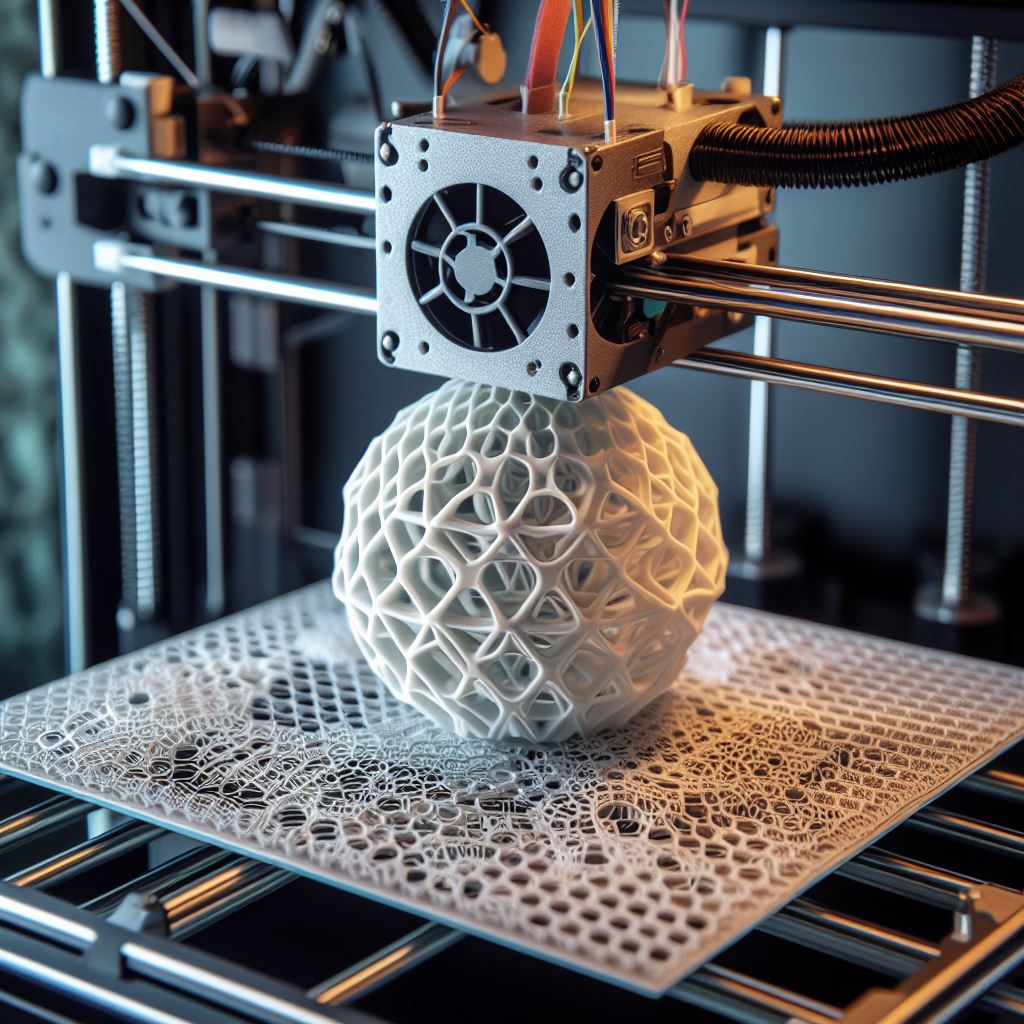
Infill is the pattern of material that fills the empty space inside a 3D printed object. It provides structural support to the object and determines its overall strength. Infill is measured as a percentage, with 0% indicating a completely hollow object and 100% indicating a solid object. The choice of infill percentage depends on the specific requirements of the print, such as strength, weight, and printing time.
How does infill affect the strength of a 3D printed object?
The infill percentage directly affects the strength of a 3D printed object. A higher infill percentage means more material is used to fill the internal structure, resulting in a stronger object. However, increasing the infill percentage also increases the printing time and material usage. Therefore, it is important to strike a balance between strength and efficiency.
What are the different infill patterns?
There are several infill patterns available in most 3D printing software, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common infill patterns include:
- Rectilinear: This pattern consists of straight lines running parallel to each other. It is easy to print and provides good strength, but it can be prone to delamination.
- Triangular: This pattern consists of triangles arranged in a grid. It offers good strength and is more resistant to delamination compared to rectilinear infill.
- Honeycomb: This pattern consists of hexagonal cells. It provides excellent strength and is lightweight, making it ideal for prints that require both strength and reduced weight.
- Grid: This pattern consists of squares arranged in a grid. It offers good strength and is easy to print, but it may not be as efficient in terms of material usage compared to other patterns.
How can you optimise infill for your prints?
To optimize infill for your prints, consider the following factors:
- Strength requirements: Determine the minimum strength required for your print and choose an infill percentage accordingly.
- Weight considerations: If weight is a concern, opt for infill patterns like honeycomb that provide good strength while reducing the overall weight of the print.
- Printing time: Higher infill percentages increase the printing time. If time is a constraint, choose a lower infill percentage that still meets your strength requirements.
- Material usage: Higher infill percentages also result in more material usage. If material cost is a concern, choose a lower infill percentage that strikes a balance between strength and efficiency.
By considering these factors and experimenting with different infill percentages and patterns, you can optimize your prints to achieve the desired strength, weight, and printing time. Remember, infill is just one of the many parameters that contribute to the quality of a 3D printed object, so it is important to consider other factors like layer height, print speed, and cooling settings as well.
With this technical guide to infill in 3D printing, you now have the knowledge to make informed decisions when it comes to optimizing your prints. Happy printing!




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.